What Is GAD? How to Identify It with Anxiety Disorder Tests
Best 2024 Guide for General Anxiety Disorder (GAD) | Testing, Treatment, and Diagnosis of GAD
It’s not unusual for people to feel anxious at times. They may be worried about a project at work or feel anxious about going to the dentist. But when those feelings of anxiety don’t go away and begin to interfere with day-to-day life, it may call for a general anxiety disorder test.
What is the generalized anxiety disorder criteria? How do you know if a person’s anxiety is considered “normal” or if there is an urgent need for a GAD mental health professional? What does GAD mean for your long-term outlook?

Anxiety Test Disorder | Diagnosis GAD
In this GAD Assessment Guide, we’ll look at different GAD questionnaire types that are used as diagnostic tools and the GAD scale for scoring anxiety. You’ll also find an overview of the basics of generalized anxiety disorder assessment, including symptoms, medications, and treatment.
When does anxiety cross the line from normal to a clinical diagnosis of anxiety disorder? A GAD screening for generalized anxiety disorder can identify the presence of anxiety that is debilitating and that requires treatment, either through psychotherapy and/or medication.
We would like to hear from you. Do you have questions about this “what’s GAD” guide? Do you know of any best practices used at your organization for managing the diagnosis anxiety disorders process or conducting GAD mental health assessments that you would like to share with the health community? If so, click here to contact the Social Work Portal Team.
See Also: Social Work Intake Forms, Assessments & Client Surveys
Table of Contents: Generalized Anxiety Disorder GAD
Keep on scrolling down this page to read each section or click any link below to go directly to that section.
- Is Anxiety a Mental Disorder?
- What Is Generalized Anxiety Disorder?
- General Anxiety Symptoms
- Causes of GAD Disorder
- How Do You Diagnose GAD?
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder Test Types
- Treatment for a Diagnosis of GAD
- Anxiety Assessment | Ways to Control Anxiety
- Conclusion | Guide to What Is a Generalized Anxiety Disorder?
- FAQ | What Is GAD Disorder
Don’t Miss: What You Need to Know About the HIPAA Form
Is Anxiety a Mental Disorder?
Anxiety, when it interferes with health and well-being, is considered a mental disorder. According to the American Psychiatric Association (APA), one or more anxiety disorders impact nearly 30% of American adults at some point in their lives.
An Anxiety diagnosis test can help mental health providers determine whether the anxiety someone feels is considered normal or has reached the threshold of being considered an anxiety disorder.
When looking up, “What’s GAD” or “anxiety disorder vs generalized anxiety disorder,” you’ll likely find similar and related diagnosis anxiety disorders in your search. Some of the main anxiety disorders are:
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
- Generalized Panic Disorder
- Social Anxiety Disorder
- Agoraphobia
- Specific Phobia
- Separation Anxiety Disorder
Related: Guide on Social Work Case Notes Example
Do you have any questions about anxiety disorder generalised, the generalized anxiety disorder definition, or anxiety disorders GAD or others? If so, click here to contact the Social Work Portal Team.
What Is Generalized Anxiety Disorder?
When you worry occasionally about work, money, kids, or other things, that doesn’t necessarily mean you have general anxiety disorder. GAD is diagnosed when an anxiety disorder assessment shows constant worrying that can’t be controlled. It usually lasts for longer than six months and interferes with normal day-to-day activities.
If you are worrying so much that you can’t concentrate, start to feel physical symptoms related to stress, and are worrying excessively and constantly, then this can indicate a general anxiety disorder.
Definition of Generalized Anxiety Disorder
According to Oxford Languages when talking about GAD mental health, the definition of generalized anxiety disorder is:
“A mental condition characterized by excessive or unrealistic anxiety about two or more aspects of life (work, social relationships, financial matters, etc.), accompanied by symptoms such as increased muscle tension, impaired concentration, and insomnia.”
Popular Article: How to Write a Social Work Soap Assessment | Guide
Would you like to know more about questions like “What does GAD stand for,” “What is HIV anxiety,” or “Do I have anxiety disorder test”? If so, click here to contact the Social Work Portal Team.
Are you looking for free social worker templates & forms? You can download all our free social worker tools here.
General Anxiety Symptoms
How do you know whether you need to take an anxiety disorder quiz to see if you’ve crossed the threshold from regular anxiety to GAD?
If you’re experiencing constant worrying and anxiety that you can’t control, it’s a good idea to talk to your doctor or mental health professional. They will likely ask anxiety disorder questions to check for some of the common symptoms.
You can also easily find sites with a GADs test online that you can take to see if you may have a mental anxiety disorder. It’s common for a GAD assessment tool to look for both mental and physical symptoms, as excessive anxiety can impact the body’s ability to function properly.
A general anxiety disorder symptoms test will look for the following symptoms of GAD:
- Unable to relax
- Constant worrying
- Inability to concentrate
- Irritability
- Fatigue
- Nausea
- Trouble falling or staying asleep
- Trembling or twitching
- Muscle tenseness
- Headaches
- Feeling nervous or restless
- Breathing rapidly
- Gastrointestinal (GI) issues
Read More: Authorization To Release Medical Records – Guide
Do you have any questions about a generalised anxiety disorder test or what an anxiety and depression scale looks like? Do you have family stress, work stress, personal stress, an upcoming stressful event, HIV anxiety, or more, and would like to share with others how you manage such stress and anxiety? If so, click here to contact the Social Work Portal Team.
Causes of GAD Disorder
During a generalized anxiety disorder assessment, several different causes may be present for constant anxiety. These can be related to your life today, to past trauma, or possibly to medications being taken for other reasons.
You may also find that the symptom of generalized anxiety disorder is hereditary and runs in the family. The point is that GAD disorder can be caused by a number of both environmental and biological factors.
Common causes of generalized anxiety disorder include:
- History of traumatic or stressful experiences (e.g., being abused or bullied as a child)
- Inherited from parents
- A side effect of medications being taken
- Drug or alcohol abuse
- Recent prolonged exposure to a stressful situation
- Excessive use of tobacco or caffeine
- A health condition, such as thyroid issues
Related: Different Process Types & Social Work Notes Documentation Examples
How Do You Diagnose GAD?
A medical or mental health professional would be the one to formally diagnose GAD. They would do this through observation, assessment of patient symptoms, and by using an anxiety diagnosis test.
Using an industry-recognized generalized anxiety disorder questionnaire, a healthcare professional can assess a patient and identify a GAD score, which will provide a level of severity for anxiety.
A GAD questionnaire PDF or online GAD screening tool will typically list a number of situations/problems and ask how often the individual has experienced these in the recent past.
For example, the questions from the GAD2 anxiety disorder test ask how often in the past two weeks a person has been bothered by:
- “Feeling nervous, anxious, or on edge”
- “Not being able to stop or control worrying”
Next, we’ll describe some common generalized anxiety disorder screening tools that are used to diagnose GAD.
Don’t Miss: How to Find Social Worker Degrees from the Best Social Work Programs
Do you have any questions about a worry and anxiety questionnaire or a generalized anxiety disorder screener? Or would you like to learn more about GAD scale scoring? Click here to contact the Social Work Portal Team.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder Test Types
There are many types of anxiety disorder questionnaire that can be used for a diagnosis of anxiety disorder. We will describe several of these GAD assessment tools below, as well as the types of lab tests done to rule out an anxiety issue.
It’s important to note that we have found the most popular of these generalized anxiety questionnaire tools to be the GAD-7, which is connected to the GAD2 anxiety test.
Below, we’ll be going through a high-level overview of the following anxiety disorders tests:
- Beck Anxiety Inventory
- GAD-2 & GAD-7 Anxiety Tests
- Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale
- Zung Self-Rating Anxiety Scale
- Lab Tests to Rule Out Other Issues
How does someone take a general anxiety disorder test?
A test to generate an anxiety score may be given by a physician, a social worker, a therapist, or another mental health or healthcare professional. It can be given as a GAD assessment PDF, an online form, or may be given verbally.
You can also find free GAD scale scoring tests online and can do a self-administered test. However, an official diagnosis of GAD needs to be done by a medical or mental health professional.
Beck Anxiety Inventory
The Beck Anxiety Inventory (BAI) was developed in 1988 (Beck, Epstein, Brown, & Steer). This is a self-report generalized anxiety disorder severity scale questionnaire that measures 21 general anxiety symptoms.
Some of the 21 symptoms asked about are:
- Numbness or tingling
- Unable to relax
- Fear of the worst happening
- Dizzy or lightheaded
- Terrified or afraid
- Feeling of choking
- Fear of losing control
For each symptom of generalized anxiety disorder, the individual taking the test will answer via multiple choice about how often they’ve felt this in the past month:
- Not at all
- Mildly but it didn’t bother me much
- Moderately – it wasn’t pleasant at times
- Severely – it bothered me a lot
Each answer will have a specific gad score between 0-3, and the total will be used for the GAD scoring interpretation.

The anxiety score range for the BAI is:
- 0 – 21 = low anxiety
- 22 – 35 = moderate anxiety
- 36 and above = potentially concerning levels of anxiety
GAD-7 & GAD-2 Anxiety Tests
The GAD-7 and GAD-2 self-report anxiety disorders tests were developed in 2006 by Drs. Spitzer, Williams, Kroenke, and colleagues, with a grant from Pfizer, Inc. This team also developed the Patient Health Questionnaire PHQ assessment tool for depression screening.
The GAD-7 and GAD-2 surveys are designed as a rapid GAD screening tool for medical professionals to use to identify the potential for debilitating anxiety that needs further intervention.
What’s the difference between GAD7 and GAD2 anxiety test disorder screening?
The number after “GAD” is for the number of questions in the GAD questionnaire. The GAD-2 anxiety disorder questionnaire uses just the first two questions that are in the seven-question GAD-7.
The GAD-2 anxiety assessment is for situations where a healthcare provider may not have much time, such as an emergency room. However, they still need to screen to see if anxiety may be a causal or contributing factor to a patient’s condition.
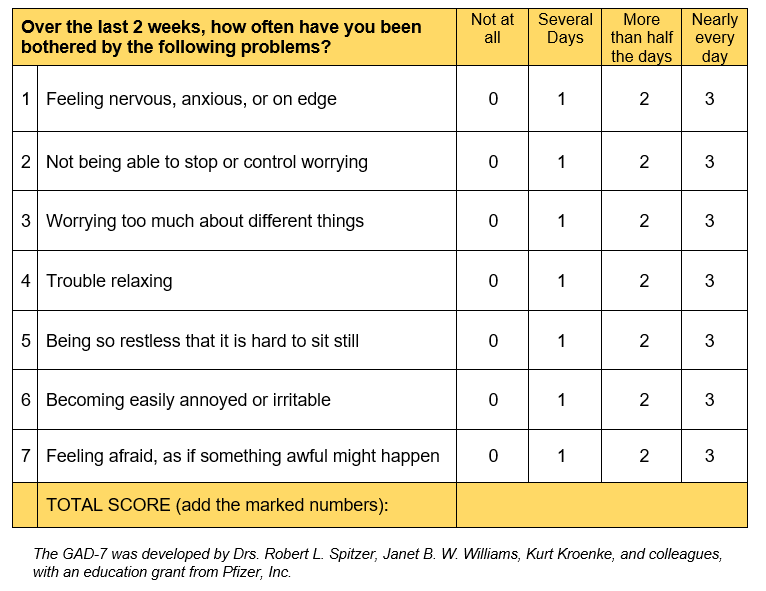
The seven questions in the GAD-7 | Generalized anxiety disorder criteria
When using the two-question GAD-2, a GAD anxiety score of 3 or more would indicate the need for further assessment. A potential next step is to administer the full seven-question GAD-7.
The GAD-7 GAD score range is as follows:
Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale
Developed by Max Hamilton in 1959, the Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HAM-A) is a questionnaire of anxiety disorder questions that clinicians can use to gauge the severity of a patient’s anxiety.
This GAD assessment scoring tool has 14 questions in categories that represent a variety of symptoms of anxiety. These include:
- Anxious mood
- Tension
- Fears
- Insomnia
- Intellectual (difficulty concentrating or poor memory)
- Depressed mood
- Somatic (muscular)
- Somatic (sensory)
- Cardiovascular symptoms
- Respiratory symptoms
- Gastrointestinal symptoms
- Genitourinary symptoms
- Autonomic symptoms
- Behavior at interview
This is not a self-report anxiety disorder test, but rather a questionnaire that the clinician will fill out. For each of the fourteen items, the clinician will use the following generalized anxiety disorder scale:
- 0= Not present
- 1 = Mild
- 2 = Moderate
- 3 = Severe
- 4 = Very severe
The generalized anxiety score will be the total of those questions. And for diagnosis GAD purposes, the following scoring system is used:
- 0-17 = Indicates mild anxiety severity
- 18-24 = Indicates mild to moderate anxiety severity
- 25-30 = Indicates moderate to severe anxiety severity
Zung Self-Rating Anxiety Scale
The Zung Self-Rating Anxiety Scale was developed by Dr. William Zung in 1971. This general anxiety disorder scoring tool is another of the anxiety disorders tests that is self-administered.
In the Zung test for anxiety disorders GAD, the individual answers 20 questions, each relating to a symptom of generalized anxiety disorder. They also indicate how often they felt this or behaved in this way during the “past several days.”
Here is an example of what the 20 generalized anxiety symptoms/questions include:
- I feel more nervous and anxious than usual.
- I feel afraid for no reason at all.
- I get upset easily or feel panicky.
- I feel like I’m falling apart and going to pieces.
- I feel that everything is all right and nothing bad will happen.
- I am bothered by headaches, neck, and back pains
- I feel weak and get tired easily
- I can breathe in and out easily
- I get bothered by stomachaches or indigestion
For each question, the individual will answer how often they are affected by it, choosing between:
- None or a little of the time
- Some of the time
- Good part of the time
- Most or all of the time
The GAD scoring interpretation uses a score between 1-4 for each answer, specific to the question. The GAD scale for this test is as follows:
- Below 45 = Within the normal range
- 45-59 = Minimal to moderate anxiety
- 60-74 = Marked to severe anxiety
- 75 and over = Most extreme anxiety
Lab Tests to Rule Out Other Issues
The diagnosis of anxiety disorder can be complicated by the fact that anxiety can cause physical symptoms, however, those physical symptoms could also be caused by other biological issues.
When reviewing results from an anxiety disorder quiz, if a clinician sees an indication of a potential biological cause for a symptom, they may give the individual lab tests to rule out a physical issue before diagnosing GAD.
These lab tests to rule out physical reasons for general anxiety symptoms can include:
- Urine tests to identify substance abuse
- Blood tests to look for thyroid hormone issues
- Endoscopy or X-ray to rule out digestive issues, such as GERD
- Chest X-ray to detect any cardiac conditions
Popular Article: Social Worker Assessment Guide for All Social Workers
Please let us know if you have any questions about a GAD survey, generalised anxiety disorder, a generalised anxiety disorder test, or any other questions about anxiety disorder generalised. Click here to contact the Social Work Portal Team.
Treatment for a Diagnosis of GAD
What does GAD mean when it comes to treatment? There are typically two paths of treatment for a diagnosis of GAD.
Psychotherapy
Psychotherapy involves working with a trained psychiatrist or psychologist to learn ways to manage anxiety. Cognitive behavioral therapy is seen as an effective way to treat a patient that’s been diagnosed due to a high GAD score.
GAD Medications
If a patient meets certain generalized anxiety disorder criteria, their medical professional may prescribe one of the GAD medications.
Some of the types of medications taken for severe generalized anxiety disorder GAD are:
- Antidepressants
- Anti-anxiety medications (such as benzodiazepines)
See Also: Assessing Risk in Social Work – Everything You Need to Know
Anxiety Assessment | Ways to Control Anxiety
One thing you may see in a generalized anxiety disorder definition is that some people have this condition chronically. Anxiety can be lessened and managed with various lifestyle changes.
Some of the lifestyle and home remedies recommended by the Mayo Clinic to control anxiety are:
- Keeping physically active
- Ensuring you get enough sleep
- Using relaxation and visualization techniques
- Eating healthy
- Avoiding recreational drugs and alcohol
- Quitting or cutting back on smoking
- Quitting or cutting back on caffeinated beverages
Don’t Miss: Why are Genograms Really Important for Social Workers?
Conclusion | Guide to What Is a Generalized Anxiety Disorder?
While nearly everyone feels anxious and worried from time to time, feeling these things constantly can indicate a more serious issue. Anxiety disorders tests help medical and mental health professionals determine if a patient may be suffering from GAD.
An individual can take a general anxiety disorder test online to see if they may be suffering from severe anxiety. However, a trained medical professional should be the one to diagnose GAD.
GAD can be a short-term or chronic condition, but there are many treatments out there, from home remedies and relaxation techniques to psychotherapy and medication for more severe cases.
Related: Clinical, Medical & Hospital Social Worker Guide
FAQ | What Is GAD Disorder
Is GAD considered a mental illness?
Anxiety, when it interferes with health and well-being, is considered a mental disorder.
What are hidden signs of generalised anxiety disorder?
Hidden signs of anxiety test disorder include those that a person may not realize are anxiety related. Some of these signs of GAD are:
•Difficulty sleeping
•Feeling tired
•Irritability
•Gastrointestinal problems
•Tense muscles
What is a symptom of generalized anxiety disorder?
A general anxiety disorder symptoms test will look for the following symptoms of GAD:
•Unable to relax
•Constant worrying
•Inability to concentrate
•Irritability
•Fatigue
•Nausea
•Trouble falling or staying asleep
•Trembling or twitching
•Muscle tenseness
•Headaches
•Feeling nervous or restless
•Breathing rapidly
•Gastrointestinal (GI) issues
How do you calm down what generalised anxiety disorder does?
Some of the lifestyle and home remedies recommended by the Mayo Clinic to control anxiety are:
•Keeping physically active
•Ensuring you get enough sleep
•Using relaxation and visualization techniques
•Eating healthy
•Avoiding recreational drugs and alcohol
•Quitting or cutting back on smoking
•Quitting or cutting back on caffeinated beverages
Note: Content on Social Works socialworkportal.com website is copyrighted.
Social Work Portal Disclaimer:
Social Work Portal is not a social work agency and we do not refer social workers. This web site is provided for educational and informational purposes only and does not constitute providing medical advice or professional services. The information provided should not be used for diagnosing or treating a health problem or disease, and those seeking personal medical advice should consult with ...
Read our full disclaimer here: Social Work Portal Disclaimer.
Image sources: Stock.adobe.com